|
*Eye injuries
associated with facial trauma
One year clinical study
Dr. FAAIZ. Y. AL-HAMDANI.
M.Sc.
Dr. k. Y. IGZEER F.F.R.C.S.I
Abstract
Patients sustained facial trauma of varous severity, whom
where admitted in medical city in baghdad were analyzed.
Total number of patients was 37.
Eye injuries were recorded, and classified into orbital and
ophthalmic inuures.
Orbital injuries were recorded as follows; enophthalmos in 7
cases (19%) traumatic telecanthus in 9 cases (24%),
circumorbital ecchymosis in 23 cases (62%), infraorbital
paraesthesia 15 cases (40%) supraorbital paraesthesia in 2
caese (5.4%), orbital emphysema in 4 cases (9.5%), lachrymal
system injry in 3 cases (8%), diplopia in 11 cases (30%).
Ophthalmic injuries; recorded as follows; pupillary reflex
defect in 3 cases (8), subconjuctival haemorrhage in 29
cases (51%), conjuctival chemosis in 4 cases (9.5%),
commotio retinnae (retinal oedema) in 2 cases (5.4%),
hyphema in one case (2.5%) , loss of vision and optic nerve
damage in 5 cases (11%) , retinal detachment in one case
(2.5%) globe rupture in one case (2.5%) , corneal injury in
one case (2.5%) and lens sublaxation in one case (2.5%).
Sixteen patients presented with bilateral fractures, thus
the no. of eyes involved were 49. It has been found that
road traffic accidents were the most common cause for facial
fractures, multiple facial fractures were a common finding.
Eye injuries recorded in 35 cases while only 2 cases were
free from both orbital and ophthalmic injuries and
circumorbital ecchymosis was the most common eye injury
recorded in the study (62%) and subconjuctival haemorrhage
the most common ophthalmic injury recorded (51%).
We concluded that serious ophthalmic injuries were not
uncommon (13.5%) complication of facial fractures which
agrees with most of previous studies, although some of these
complications resulted from unusual types of fracture zygoma,
which is unusual finding compared with other studies.
*Presented in the 20th conference of Iraqi dental
association 2000.
|
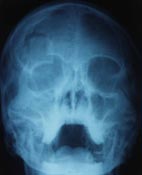
occipito mental view ;
inward displacement of RT frontal bone & radiopacity of RT maxillary sinus |
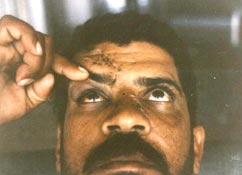
extended Lefort ,
blow out fracture RT side &
zygomatic bone fracture LT side notice the limitation in upward gaze RT
side |
رجوع
|

